NEWS INSIDE BODIES & MINDS

Incredible things are now possible inside our bodies. New technologies using light, biological transistors, and biopatches can help keep your insides healthy better than ever before. We took a look at a few of the most promising.
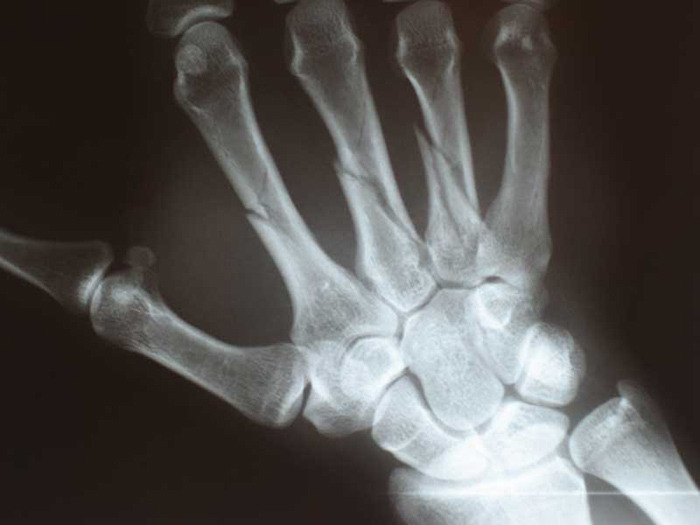 Image: Courtesy of JVinocur. Metacarpal Fractures.
Image: Courtesy of JVinocur. Metacarpal Fractures.
Now, you can grow new bone inside your body. University of Iowa researchers have created a “bio patch” that regenerates bone tissue.
It has been demonstrated to completely regrow bone in mouse test subjects and to stimulate growth in human cells, as reported in Biomaterials.
 Image: Courtesy of Conscious Life News. Stem Cells.
Image: Courtesy of Conscious Life News. Stem Cells.
The team, led by Satheesh Elangovan, used microscopic plasmid particles, embedded with pieces of DNA specifically related to producing growth. They delivered bone-producing instructions to existing bone cells inside a living body. The bone cells then followed these instructions and began to produce the required proteins for more bone production.
Video: Courtesy of VUTChempoint.
In order to grow the new bone as a perfect fit, researchers made a collagen scaffold in the desired shape, loaded it with the plasmid particles, and inserted it in the target area, where the repair would take place. The bone was completely regenerated in a healthy, normal shape in about four weeks. The biopatch was also able to stimulate new growth in human bone marrow stromal cells.
Imagine what this patch might do to help repair bone injuries and deformities. Birth defects involving missing bone around the head or face and dental applications, such as rebuilding jaw bone to prevent tooth loss or support implants, are just a few of the exciting possibilities.
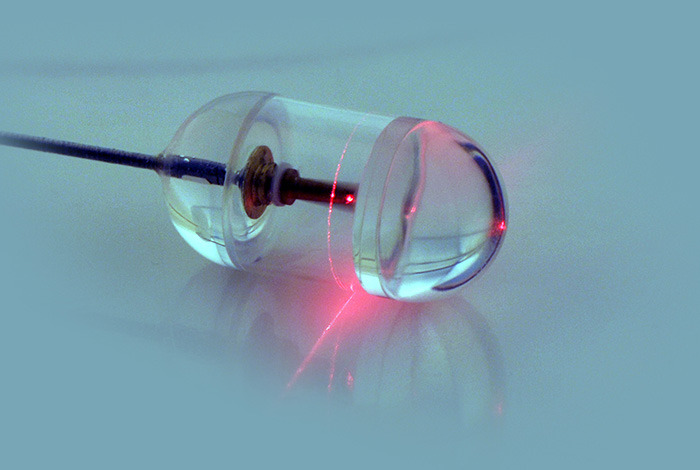 Photo: Michalina Gora. Courtesy of Massachusetts General Hospital. Endomicroscopy capsule.
Photo: Michalina Gora. Courtesy of Massachusetts General Hospital. Endomicroscopy capsule.
Light is also being used now to help doctors get a better look at the inside of your throat.
Researchers at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have developed an imaging system enclosed in a capsule about the size of a multivitamin pill that creates detailed, three-dimensional microscopic images of the esophageal wall.
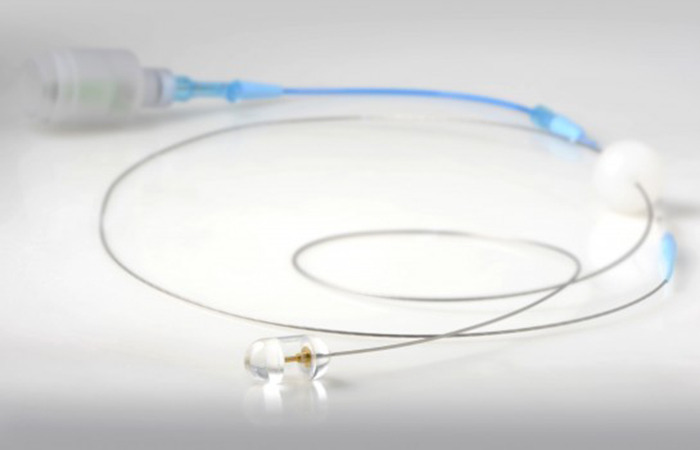 Photo: Courtesy of Tearney Lab. GI Capsule with tether.
Photo: Courtesy of Tearney Lab. GI Capsule with tether.
The capsule is attached to a tether that connects to the imaging console. The capsule is swallowed by a patient, and it can be controlled by technicians to move up and down through the esophagus to capture the desired images.
This new system offers major advantages over traditional endoscopy. You don’t have to be sedated. It can be performed in a doctor’s office. And it gives doctors way more detailed information so they can better detect and diagnose problems, according to a report in Nature Medicine.
 Image: Courtesy of Photonics Workshop.
Image: Courtesy of Photonics Workshop.
Light can communicate with cells inside your body and tell them what to do.
This has been limited due to the fact that light cannot pass through tissue sufficiently deep enough to be of much use. But now, researchers at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital have created a method to deliver light signals to tissue deep inside the body, using a light-guiding hydrogel.
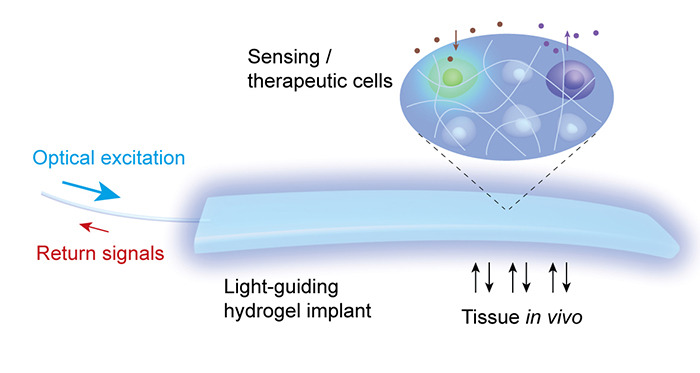 Image: Courtesy of Harvard Bio-Optics Lab. Hydrogel Implant.
Image: Courtesy of Harvard Bio-Optics Lab. Hydrogel Implant.
They created a polymer-based scaffold to support a group of cells genetically engineered to emit or respond to light when subjected to certain metabolic signals. An optical fiber connects the implant to either an external light source or a light detector.
 Photo: Bryce Vickmark. Implantable sensor.
Photo: Bryce Vickmark. Implantable sensor.
In diabetic mice, the application of light was shown to improve their condition by increasing the levels of a protein called GLP-1, which plays a role in glucose metabolism, as reported in Nature Photonics.
 Image: Ed Boyden. Courtesy of Sputnik Animation. Optigenetics
Image: Ed Boyden. Courtesy of Sputnik Animation. Optigenetics
Light is also now being used for other therapies, such as optigenetics, which treats disorders by using different colored light signals to activate and deactivate braincells.
Now that light can go deep inside, imagine what it can do to detect and cure disease, all with higher degree of accuracy and without the risks and negative effects of chemical or surgical interventions.
 Image: Courtesy of Extreme Tech.
Image: Courtesy of Extreme Tech.
Now "radios" inside your body can tune you up! Researchers at Stanford University just created biological transistors, made entirely out of genetic material. In a paper recently published in Science, the team reported using a biological transistor, or "transcriptor," made of DNA and RNA, in place of gears or electrons.
 Photo: Courtesy of The Independent.
Photo: Courtesy of The Independent.
These transcriptors, can regulate and control a living cell. They can, for example, tell a cancer cell to stop multiplying. They can tell cells to accept certain medicines. They can tell cells to heal.
 Photo: Courtesy of The Science of Reality.
Photo: Courtesy of The Science of Reality.
This development is a leap towards building a biological computer that can live inside the body and sense its surroundings, and then manipulate its host cells into performing as desired. Pharmaceuticals might become obsolete.
To help develop the biological computer more quickly, lead researcher, Drew Endy, and his team have contributed their information to the public domain.
Read more about Beautiful Insides, as they relate to Arts/Design, Nature/Science, Food/Drink, Place/Time, Mind/Body, and Soul/Impact, includinng Beautiful Inside Stories, Beauty Inside Ancient Cores, Beautiful Insides to Admire & Taste, Intimate Surreal Insides, and Inside the Best Places Now.
Get busy and enter the BN Competitions, Our theme this week is Beautiful Insides. Send in your images and ideas. Deadline is 11.17.13.
Image: Courtesy of InterActiveMediaSW.
Also, check out our special competition: The Most Beautiful Sound in the World! We are thrilled about this effort, together with SoundCloud and The Sound Agency. And we can’t wait to hear what you’ve got!







